Compression at an angle to the grain
Checks a cross-section in compression at an angle to the grain according to Clause 6.2.2.
All references to EN 1995-1-1:2004+A2:2014 unless otherwise stated.
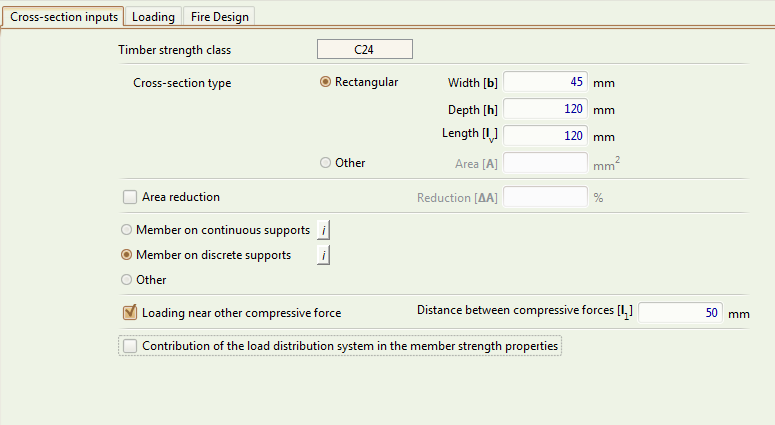
Cross-section Inputs tab
Timber class
The timber strength class of the cross-section. See the timber database page for the types supported by Teretron.
Cross-section type
The geometry type of the cross-section.
Width
The width of a rectangular cross-section, in mm.
Depth
The depth of a rectangular cross-section, in mm.
Length
The distribution length of the compressive force, in mm.
Area
The area of a generic cross-section, in .
Area reduction
The area reduction ΔA refers to reductions in the nominal cross-section size that have to be taken into account in the calculation of the member strength (e.g. holes from fasteners) according to Subclause 5.2(2).
It should be given as a percentage of the total nominal area of the cross-section.
Calculation of factor
Eurocode 5 states that the compressive strength can be multiplied by a factor for rectangular cross-sections of solid or glulam softwood, with . This factor takes into account the load configuration, the possibility of splitting, and the degree of compressive deformation.
The value of should be taken between 1.0 and 1.75 and its precise value depends on the support conditions and the loading type.
The support condition cases are:
Member on continuous supports
For a beam resting on continuous supports, as per Figure 6.2(a).
Member on discrete supports
For a beam on discrete supports, as per Figure 6.2(b).
Other
Member arrangements not covered by the two cases above.
You can click the symbol next to each design case to see a pop-up with the respective image.
The loading cases are:
Loading near the edge
The distance to the edge must be specified, in mm.
Loading near the compressive force
The distance between compressive forces must be specified, in mm.
Contribution of the load distribution system in the member strength properties
Includes factor for the calculation of the member strength, according to Clause 6.6, for a member that functions as part of a continuous load distribution system.
Note that Subclause 6.6(3) states that the strength verification for a continuous load distribution system should be carried out assuming short-term load duration.
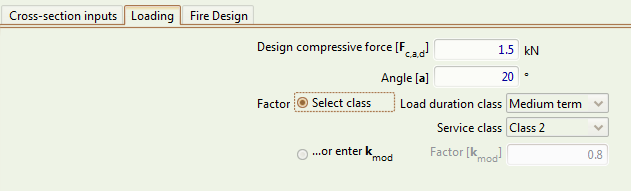
Loading Inputs tab
Design compressive force
The design value of the compressive force acting on the cross-section at an angle to the grain, in kN.
Angle
The angle of the axis of the compressive force to the grain, in degrees.
Load duration class
The Load Duration Class, as defined in Clause 2.3.1.2.
Service class
The Service Class, taking into account the temperature and relative humidity of the environment, as described in Clause 2.3.1.3.
Factor taking into account the effect of the duration of the loads and the moisture content, according to Clause 3.1.3.
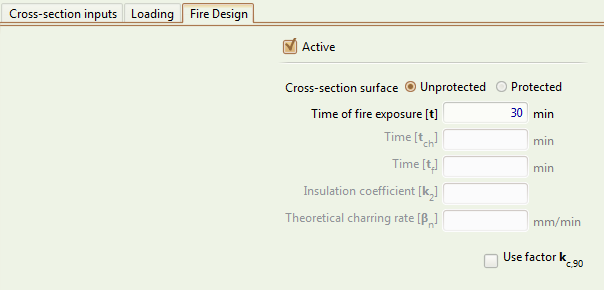
Fire Design tab
Active
Selects if this cross-section will also be designed against fire.
Cross-section surface
Defines if the cross-section surface is unprotected (exposed to fire on all sides) or is protected (on all sides).
Time of fire exposure t
The time of the exposure of the cross-section to fire, in minutes.
Time
The time of exposure of a protected cross-section to fire until it starts to char, in minutes.
Time
The time of exposure of a protected cross-section to fire until the protection fails completely, in minutes.
Note that this is can be longer (but not shorter) than .
Factor
Factor defines the charring rate of a protected cross-section between the time it starts to char and the time the protection fails completely.
It is required when has a different value to .
Theoretical charring rate
The theoretical charring rate of the timber, in mm per minute.
It is required for plywood where the relevant standards do not provide a default value.
Remaining cross-section
The remaining cross-section for the fire design time, in . This option appears only when a generic cross-section has been selected.
Use factor
If checked, the factor is included in the fire design calculations.